Symptom : Swollen Lymph Nodes Achy Muscles And Joint Pain
Lymph nodes are part of your bodys immune system and protect your blood by getting rid of bacteria and viruses. They tend to get inflamed when theres an infection. Many of them are located in your armpit, groin and neck which can result in aches and pains in these areas.
Given these symptoms are common across many viral infections, they alone are not a reliable way to determine if the infection you are experiencing is HIV.
What Are The Treatments For Hiv/aids
There is no cure for HIV infection, but it can be treated with medicines. This is called antiretroviral therapy . ART can make HIV infection a manageable chronic condition. It also reduces the risk of spreading the virus to others.
Most people with HIV live long and healthy lives if they get and stay on ART. It’s also important to take care of yourself. Making sure that you have the support you need, living a healthy lifestyle, and getting regular medical care can help you enjoy a better quality of life.
What Can I Expect If I Have Hiv
If youre diagnosed with HIV, its important to know that those living with HIV who follow treatment guidelines can live full lives for nearly as long as those without HIV.
If you have a high CD4 count and an undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, research suggests youll have the best outcomes, as long as you continue your treatment plan.
You can improve your outlook by:
- Getting tested as part of routine healthcare or if you think youve been exposed.
- Starting ART soon after being diagnosed.
- Taking your medicine every day.
- Keeping your appointments with your healthcare team.
ART can keep blood levels undetectable but cant entirely rid your body of the virus . If you dont take your medication every day, the virus can start multiplying again and mutate, which may cause your medications to stop working.
Left untreated, it can take about 10 years for HIV to advance to AIDS. If you progress to AIDS and it goes untreated, you can expect to live about three years more.
For those on treatment, if you have a high CD4 count and undetectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you can expect to live about as long as someone without HIV. If you have a low CD4 count or a detectable viral load within a year of starting treatment, you may live 10 to 20 years less than someone without HIV.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Test Be Wrong
Serum Testing For Antigen And Antibody
Patients with suspected acute human immunodeficiency virus infection should undergo serum testing for HIV antibody and HIV antigen using HIV nucleic acid amplification, HIV p24 antigen, fourth-generation enzyme-linked immunoassay , or polymerase chain reaction testing for viral load. Beware of false-positive HIV viral load test results . For more information, see Rapid Testing for HIV and Laboratory Assays in HIV Infection.
How Hiv Affects The Body

HIV attacks the immune system. It specifically attacks the CD4 cells, a subtype of a T cell group. T cells help the body fight off infections.
Without treatment, HIV reduces the number of CD4 cells in the body, increasing a persons risk of getting infections. If HIV develops to stage 3, they will also have a higher chance of developing cancer.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provide information on where individuals can find their nearest HIV testing center.
You May Like: Does Hiv Have Any Symptoms
If I Have Hiv How Can I Keep From Spreading It To Others
The best ways to keep from spreading HIV to others are many of the same ways you use to protect yourself:
- Let sexual partners and anyone you inject drugs with know that you have HIV.
- Follow your treatment plan and dont miss medications. If you have an undetectable viral load, you greatly reduce the risk of transmitting HIV through sex.
- Talk to your sexual partner about taking PrEP.
- Wear condoms for vaginal, anal and oral sex even if you have an undetectable viral load.
- Dont share needles or other equipment to inject drugs.
- Limit the number of sexual partners you have.
- If youre pregnant and have HIV, following your treatment plan, including ART medications, can reduce your risk of transmitting the virus to your child.
Progressing To Stage 3 Hiv
If a person with HIV does not receive treatment, the condition may eventually progress to stage 3 HIV, also known as AIDS. Thanks to modern medical advances, current HIV infections rarely reach stage 3 in the U.S.
Stage 3 HIV is not a specific disease but a syndrome with a wide range of identifiable symptoms. The symptoms can also stem from other illnesses because opportunistic infections take advantage of the bodys reduced immune activity.
Symptoms include:
Treatment will depend on the individual and their complications. The persons healthcare team will help them make a suitable plan.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Window Period For Hiv
Tests For Other Abnormalities
In patients with HIV myopathy, EMG is a sensitive diagnostic test. The most common finding on muscle biopsy is scattered myofiber degeneration with occasional inflammatory infiltrates. Other pathologic findings include nemaline rod bodies, cytoplasmic bodies, and mitochondrial abnormalities. Serial creatine kinase levels are useful for monitoring the course of the disorder.
EMG is useful for evaluating mononeuritis multiplex. Results generally reveal multifocal axonal neuropathy. Biopsy of nerve tissue reveals inflammation and vasculitis. In some cases, CMV inclusions have been found.
In patients with elevated transaminases, acute viral hepatitis A, B, and C should be excluded with appropriate serologic testing.
Symptom : Fatigue And Headache
The inflammatory response generated by your besieged immune system can cause you to feel tired and lethargic. Sometimes it can make you feel winded while walking or generally feel out of breath. Fatigue can be both an early and later symptom of HIV.
There are several things that can cause a person to feel fatigued, so pay attention to your body and your lifestyle to see if you can draw a conclusion. If your fatigue persists, seek advice from your doctor.
You May Like: Can You Tell If You Have Hiv
How Can A Woman Reduce Her Chances Of Contracting Hiv
HIV is transmitted through bodily fluids like blood and semen. Using injection drugs, having unprotected sex and having multiple sex partners increases the chances of acquiring HIV. The only way to be absolutely certain you do not become infected with HIV is to not have sex and not use injection drugs. You also can avoid infection by only having one sex partner as long as your partner does not have HIV and has sex only with you. According to the Centers For Disease Control and Prevention , using a male or female condom every time you have vaginal or anal sex can greatly lower your risk of infection. Using condoms for oral sex will reduce your risk for other STDs as well. It also is important not to douche, since douching removes some of the normal vaginal bacteria that can protect you from infection.
The Asymptomatic Stage Of Hiv
Once seroconversion is over, most people feel fine and dont experience any symptoms. This is often called the asymptomatic stage and it can last for several years.
Though you might feel well at this stage, the virus is active, infecting new cells, making copies of itself and damaging your immune systems ability to fight illness.
Don’t Miss: How Long Does It Take For Hiv Symptoms To Start
How Is Acute Hiv Infection Treated
Proper treatment is crucial for people diagnosed with HIV.
Healthcare providers and scientists agree that early treatment with antiretroviral drugs should be used by all HIV-positive people who are ready to start taking a daily medication.
Early treatment may minimize the viruss effects on the immune system.
Newer antiretroviral medications are usually very well tolerated, but theres always the possibility of side effects.
If a person thinks theyre experiencing a side effect of or an allergic reaction to their medication, they should immediately contact their healthcare provider.
In addition to medical treatment, healthcare providers may also suggest certain lifestyle adjustments, including:
Theres no cure for HIV, but treatment allows people with HIV to live long and healthy lives. The outlook is best for people who begin treatment before HIV has damaged their immune system.
Early diagnosis and the right treatment help prevent HIV progressing to AIDS.
Successful treatment improves both the life expectancy and quality of life of someone living with HIV. In most cases, HIV is considered a chronic condition and can be managed long term.
Treatment can also help someone living with HIV reach an undetectable viral load, at which point theyll be unable to transmit HIV to sexual partners.
Acute HIV infection can be prevented by avoiding exposure to the blood, semen, anal secretions, and vaginal fluid of a person living with HIV.
Diagnosing Hiv Infection & Aids

Doctors at NYU Langone diagnose human immunodeficiency virus, known as HIV, a chronic viral infection that destroys certain infection-fighting white blood cells. If left untreated, HIV weakens the immune system, so the body is unable to fight infections and disease. When this occurs, HIV infection leads to a chronic, possibly life-threatening illness called acquired immunodeficiency syndrome, or AIDS.
HIV is transmitted through sex by sharing needles, syringes, or other equipment through contact with infected blood or through pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
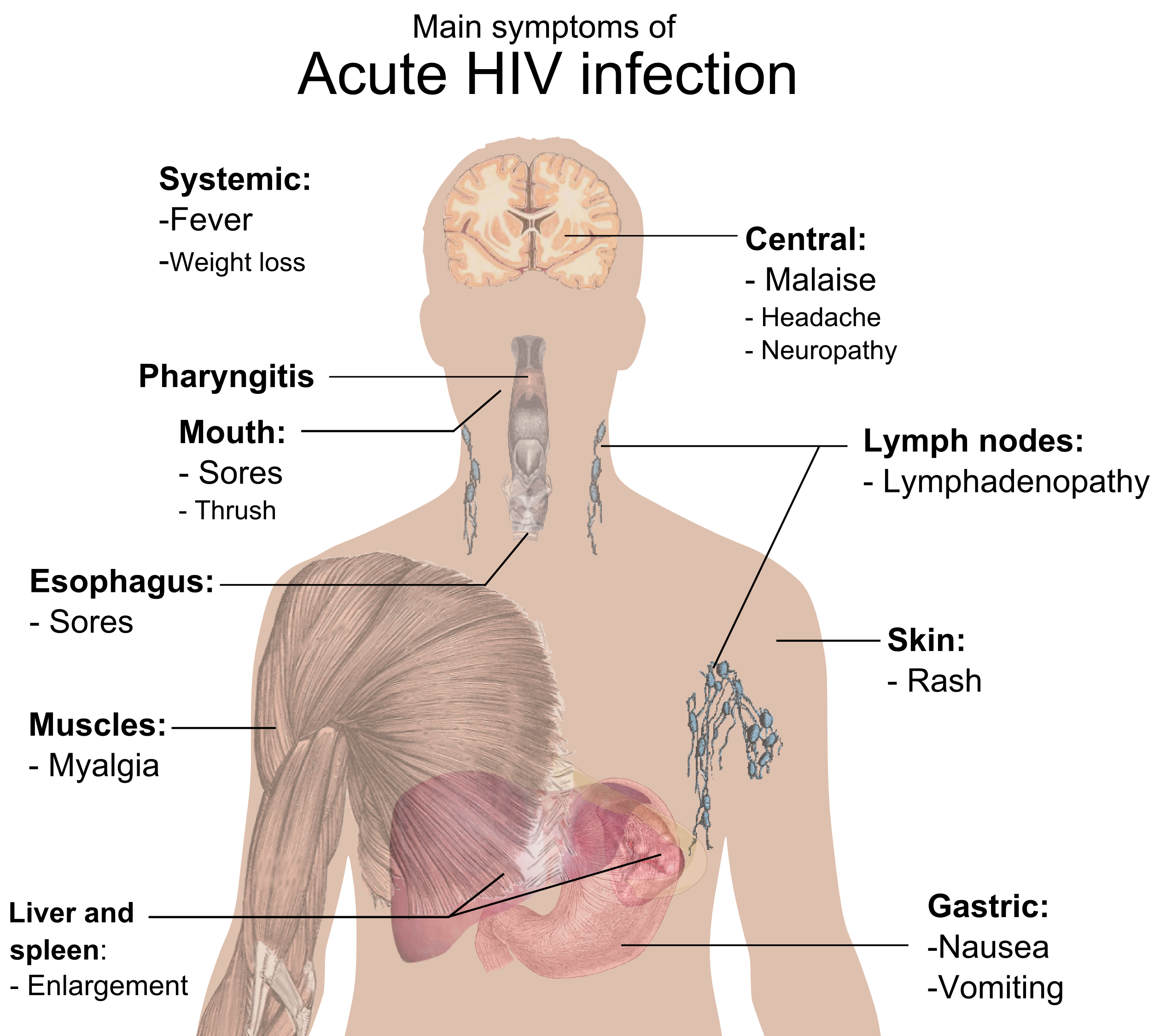
A few weeks to three months after becoming infected with HIV, many people develop intense flu-like symptoms, such as fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. They may also experience weight loss and night sweats during this initial phase. However, many people who are infected with the virus have no symptoms for 10 years or longer.
After the initial phase of an HIV infection, the disease moves into a period called clinical latency. This means the virus is developing but is producing few if any mild symptoms. Even when it causes no symptoms, the virus can be transmitted to others.
As HIV multiplies and destroys certain white blood cellsthe CD4 cells, which fight bacteria and virusesa person may develop symptoms of infection. These might include recurring fever, intense night sweats, and prolonged swelling of lymph glands in the armpits, groin, or neck. Sores in the mouth, anus, or genitals may also occur.
Also Check: Can You Get Hiv From Receiving Oral Sex
Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
You can reduce the risk of spreading HIV by:
- Getting tested for HIV.
- Choosing less risky sexual behaviors. This includes limiting the number of sexual partners you have and using latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
- Getting tested and treated for sexually transmitted diseases .
- Not injecting drugs.
- Talking to your health care provider about medicines to prevent HIV:
- PrEP is for people who don’t already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk.
- PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. It is only for emergency situations. PEP must be started within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV.
NIH: National Institutes of Health
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they won’t work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive person’s CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
Recommended Reading: How Early Can You Detect Hiv
What Is The Difference Between Hiv And Aids
The term AIDS refers to the most advanced stages of HIV infection. Most of the conditions affecting people with AIDS are opportunistic infections that generally do not affect healthy people. In people with AIDS, these infections are often severe and sometimes fatal because the immune system is so ravaged by HIV that the body cannot fight off the infection. Symptoms of opportunistic infections common in people with AIDS include:
- coughing and shortness of breath
- seizures and lack of coordination
- difficult or painful swallowing
- severe headaches
- coma
People with AIDS also are particularly prone to developing various cancers. These cancers are usually more aggressive and difficult to treat in people with AIDS.
When Is Hiv Contagious
In the early stage of HIV transmission, the levels of the virus in the blood and semen are high. A person can easily transmit the virus during this time. Additionally, transmission is more likely during this primary acute stage than in the following stage.
During the clinical latency stage, a person with HIV experiences fewer symptoms. However, they can still transmit the virus to others.
According to the CDC, a person with an undetectable viral load cannot transmit HIV to another individual. This is because HIV treatment suppresses the virus, leaving a low presence of the virus in the blood.
When HIV is not detectable in a test, it is not transmissible.
You May Like: How Does Aids Develop From An Hiv Infection
How Long Does It Take To Show Symptoms Of Hiv
Some people notice flu-like symptoms 1-4 weeks after they’re first infected. They often only last a week or two. This stage is called acute or primary HIV infection.
Then, you may go for 10 years or more without further symptoms. This is called asymptomatic HIV infection. Even though you feel fine, the virus is still active in your body. And you can still give it to someone else.
Once HIV has seriously harmed your immune system, you’re at risk for diseases that a healthy body could fight off. In this stage, symptomatic HIV infection, you start to notice problems caused by those “opportunistic” infections.
How Can I Reduce My Risk Of Getting Hiv
The best way to reduce your risk of HIV is to be aware of how it spreads and protect yourself during certain activities. Having sex without a condom and sharing needles to take drugs are the most common ways that HIV spreads.
These are some ways to reduce your risk:
- Use latex condoms whenever you have any type of sex .
- Don’t use condoms made from animal products .
- Use water-based lubricants .
- Never share needles to take drugs.
- Get tested and treated for other STDs. Other STDs can put you at higher risk for an HIV infection.
- Avoid getting drunk or high. Intoxicated people might be less likely to protect themselves.
- If you are at high risk of HIV exposure, ask your healthcare provider if you should be taking pre-exposure prophylaxis .
- If you think youve been exposed to HIV, contact your healthcare provider as soon as possible to see if you should take post-exposure prophylaxis .
- Consider getting tested to know if you can pass HIV to others.
It’s important to use a condom correctly to protect yourself against HIV. Use a male condom for any sex act that involves your penis.
You can also protect the vagina or anus with dental dams or internal condoms. Dental dams are flat pieces of polyurethane or latex that you can put over your vagina or anus if you are having oral sex. An internal condom can be used by insertion into your vagina or anus.
You should only use one type of condom at a time. Do not use both a male condom and an internal condom.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv If Both Partners Are Negative
If I Am Pregnant And Have Hiv Will My Baby Also Have Hiv
Most women with HIV can protect their baby from becoming infected during pregnancy. Proper pre-natal treatment can reduce the risk that an HIV-positive mother will pass the virus to her child to less than 1 percent. The only way these special treatments can be provided is if the health care professionals know the mother is living with HIV. Treatment is most effective when started early in pregnancy. HIV-positive moms should not breastfeed their babies because HIV is sometimes passed this way.
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for a reduced cost or for free.
Also Check: How Long Does It Take For Hiv Symptoms To Develop
How Common Is Hiv Infection
In some areas of the world, such as in sub-Saharan Africa, rates of HIV infection are extremely high and continue to rise rapidly. Worldwide, it is estimated that 42 million people are living with HIV/AIDS. In 2002 alone, 5 million people became infected with HIV, and more than 3 million died from AIDS. Many infected people live in impoverished areas where medicines and other treatments are not available or affordable.
In the United States, HIV infection is less common. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , by the end of 2001 a total of about 816,000 cases of AIDS had been reported and about 468,000 deaths had been attributed to AIDS since the disease was first recognized. More than 9,000 children in the United States under the age of 13 are living with AIDS. The infection is spreading most rapidly among people of African ancestry and people of Latino ancestry, especially among young men. As with other sexually transmitted diseases , teens and young adults are at higher risk for contracting HIV infection because they are more likely to have unprotected sex. Approximately one-third of people worldwide with HIV or AIDS are 15 to 24 years old.
Since 1987 the AIDS Memorial Quilt has underscored the devastating impact of the disease. Each of the more than 44,000 panels memorializes the life of someone who has died of AIDS. Paul Margolies