What Are The Types Of Hiv/aids Medicines
There are several different types of HIV/AIDS medicines. Some work by blocking or changing enzymes that HIV needs to make copies of itself. This prevents HIV from copying itself, which reduces the amount of HIV in the body. Several medicines do this:
- Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors block an enzyme called reverse transcriptase
- Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors bind to and later change reverse transcriptase
- Integrase inhibitors block an enzyme called integrase
- Protease inhibitors block an enzyme called protease
Some HIV/AIDS medicines interfere with HIV’s ability to infect CD4 immune system cells:
- Fusion inhibitors block HIV from entering the cells
- CCR5 antagonists and post-attachment inhibitors block different molecules on the CD4 cells. To infect a cell, HIV has to bind to two types of molecules on the cell’s surface. Blocking either of these molecules prevents HIV from entering the cells.
- Attachment inhibitors bind to a specific protein on the outer surface of HIV. This prevents HIV from entering the cell.
In some cases, people take more than one medicine:
- Pharmacokinetic enhancers boost the effectiveness of certain HIV/AIDS medicines. A pharmacokinetic enhancer slows the breakdown of the other medicine. This allows that medicine to stay in the body longer at a higher concentration.
- Multidrug combinations include a combination of two or more different HIV/AIDS medicines
Testing Positive For Hiv
If you test positive, your doctor will complete a medical history and physical exam.
He or she may order several lab tests to check your overall health, including:
- A complete blood count , to identify the numbers and types of cells in your blood.
- A chemistry screen, to measure the blood levels of certain substances and to see how well your liver and kidneys are working.
Other tests may be done to check for current or past infections that may become worse because of HIV. You may be tested for:
Common Questions & Answers
HIV is an abbreviation that stands for human immunodeficiency virus. If you are HIV positive it means that an HIV test has detected the presence of the virus in your body. HIV attacks your body’s immune system.
AIDS is an acronym that stands for the disease caused by HIV, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. It is a late stage of infection in which the HIV virus has actively damaged the immune system.
Read Also: Does Youngboy Really Have Herpes
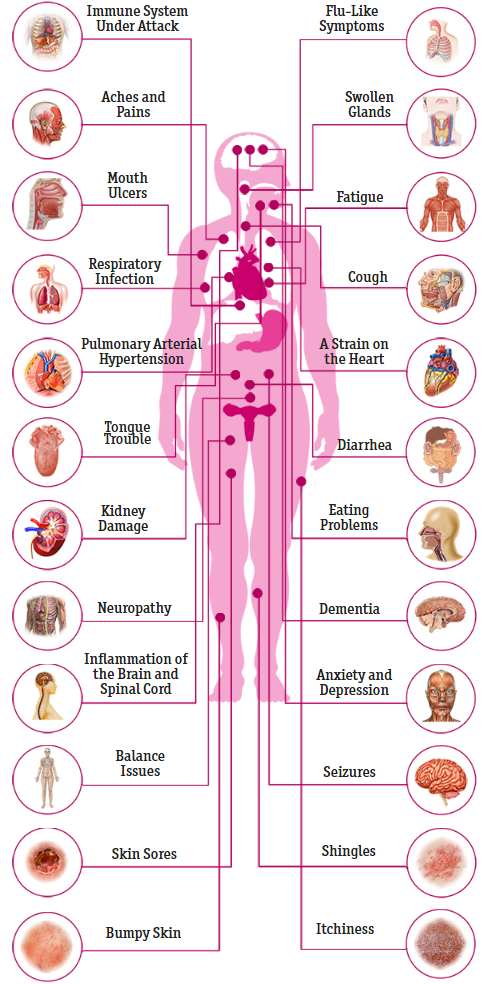
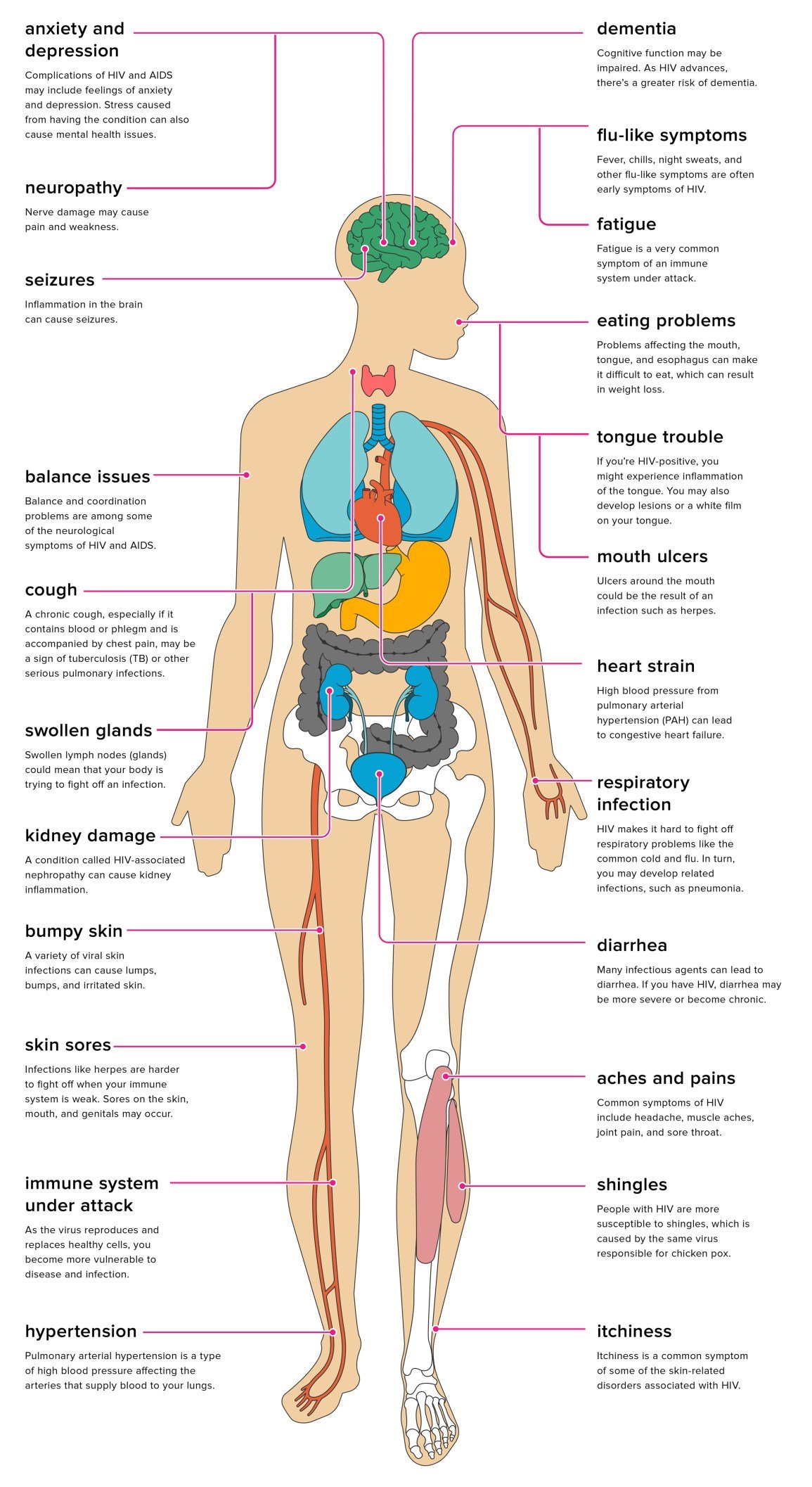
What Does Hiv Pain Feel Like
HIV-related pain Types of pain that commonly affect people with HIV include: Headache: Pain can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by intense pressure, tightness, or throbbing sensations. headaches are common when CD4 cell counts are low, infections occur, or other HIV-related illnesses are present.
Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to keep your immune system strong. Heart-healthy eating can help prevent some of the problems, such as high cholesterol, that can be caused by treatment for HIV.
- Learn how to deal with the weight loss that HIV infection can cause.
- Learn how to handle food properly to avoid getting food poisoning. For more information, see the topic Food Poisoning and Safe Food Handling.
- Exercise regularly to reduce stress and improve the quality of your life. Take steps to help prevent HIV-related fatigue.
- Don’t smoke. People with HIV are more likely to have a heart attack or get lung cancer.footnote 22, footnote 23 Cigarette smoking can raise these risks even more.
- Don’t use illegal drugs. And limit your use of alcohol.
Read Also: How Long From Hiv To Aids
What Are The Factors That Affect Disease Progression
The most important factor affecting HIV progression is the ability to achieve viral suppression. Taking antiretroviral therapy regularly helps many people slow the progression of HIV and reach viral suppression.
However, a variety of factors affect HIV progression, and some people progress through the phases of HIV more quickly than others.
Factors that affect HIV progression can include:
- Ability to achieve viral suppression. Whether someone can take their antiretroviral medications and achieve viral suppression is the most important factor by far.
- Age when symptoms start. Being older can result in faster progression of HIV.
- Health before treatment. If a person had other diseases, such as tuberculosis, hepatitis C, or other sexually transmitted diseases , it can affect their overall health.
- Timing of diagnosis. Another important factor is how soon a person was diagnosed after they contracted HIV. The longer between their diagnosis and treatment, the more time the disease has to progress unchecked.
- Lifestyle. Practicing an unhealthy lifestyle, such as having a poor diet and experiencing severe stress, can cause HIV to progress more quickly.
- Genetic history. Some people seem to progress more quickly through their disease given their genetic makeup.
Some factors can delay or slow the progression of HIV. These include:
Living a healthy lifestyle and seeing a healthcare provider regularly can make a big difference in a persons overall health.
Mechanism Of Hiv Infection
Once in the body, HIV attaches to several types of white blood cells. The most important are certain helper T lymphocytes involves white blood cells that travel through the bloodstream and into tissues, searching for and attacking microorganisms and… read more ). Helper T lymphocytes activate and coordinate other cells of the immune system. On their surface, these lymphocytes have a receptor called CD4, which enables HIV to attach to them. Thus, these helper lymphocytes are designated as CD4+.
). Once inside a CD4+ lymphocyte, the virus uses an enzyme called reverse transcriptase to make a copy of its RNA, but the copy is made as deoxyribonucleic acid that contain the code for a specific protein that functions in one or more types of cells in the body. Chromosomes are structures within cells… read more ). HIV mutates easily at this point because reverse transcriptase is prone to making errors during the conversion of HIV RNA to DNA. These mutations make HIV more difficult to control because the many mutations increase the chance of producing HIV that can resist attacks by the persons immune system and/or antiretroviral drugs.
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
Why Does The Immune System Fail To Fight The Hiv Virus
There are various reasons which can contribute to the failure of the immune system to control HIV infection and prevent AIDS development. By infecting CD4+ T cells, HIV is able to replicate predominantly in activated T cells and paralyse one of the main components of adaptive immune system. HIV can also establish latent infection in CD4+ T cells and remain invisible to CD8+ T cells and therefore replication can occur later in the infection and generate new virions. Antigenic mutation within the T-cell epitopes can affect the binding capacity of MHC molecules to the viral peptides, resulting in the inability of the TCRs to recognise the MHC-peptide complex. Finally, HIV is able to hide from anti-HIV antibodies by expressing non-immunogenic glycans on key antibody epitopes.
Hiv Effects On The Circulatory System
Several things make your chances of heart-related problems go up. Because HIV affects your immune system, your body will be inflamed as it tries to fight the infection, like itâs on a constant simmer. This kind of inflammation has been linked to heart disease.
Some drugs you take for HIV can also make heart disease more likely. They can cause insulin resistance, which makes you more likely to get diabetes, and problems breaking down fats. Diabetes, in turn, raises your risk of heart disease. You might need medicines to control your blood sugar and cholesterol.
If you smoke, quit. Eat a variety of vegetables and fruits, plenty of whole grains, and foods with omega-3 fatty acids. Choose lean cuts of meat and low-fat dairy products. Exercise, like taking a brisk walk, for 20 to 30 minutes most days of the week.
If you’re carrying extra weight, losing as little as 5 or 10 pounds could make a big difference.
Also Check: How Long After Contracting Hiv Do You Get Symptoms
If You Already Have Hiv
If you are infected with HIV, you can greatly lower the risk of spreading the infection to your sex partner by starting treatment when your immune system is still healthy.
Experts recommend starting treatment as soon as you know you are infected.footnote 19
Studies have shown that early treatment greatly lowers the risk of spreading HIV to an uninfected partner.footnote 20, footnote 21
Your partner may also be able to take medicine to prevent getting infected.footnote 15 This is called pre-exposure prophylaxis .
Steps to prevent spreading HIV
If you are HIV-positive or have engaged in sex or needle-sharing with someone who could be infected with HIV, take precautions to prevent spreading the infection to others.
- Take antiretroviral medicines. Getting treated for HIV can help prevent the spread of HIV to people who are not infected.
- Tell your sex partner or partners about your behavior and whether you are HIV-positive.
- Follow safer sex practices, such as using condoms.
- Do not donate blood, plasma, semen, body organs, or body tissues.
- Do not share personal items, such as toothbrushes, razors, or sex toys, that may be contaminated with blood, semen, or vaginal fluids.
How Hiv Is Not Spread
The virus doesn’t survive well outside the body. So HIV cannot be spread through casual contact with an infected person, such as by sharing drinking glasses, by casual kissing, or by coming into contact with the person’s sweat or urine.
It is now extremely rare in the United States for HIV to be transmitted by blood transfusions or organ transplants.
Read Also: Do Nba Youngboy Have Herpes
Stages Of Hiv Infection
About a month after you get HIV, you might feel like you have the flu. This is the first stage, called primary or acute HIV infection. Symptoms include:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
The next stage is called clinical latency, or chronic infection. You might have no symptoms, or only mild ones, for 10 years or more.
Without treatment, as HIV keeps multiplying inside your body, youâll move into the third stage, which is AIDS. A person who has HIV is diagnosed with AIDS when they have fewer than 200 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter of blood or when they get whatâs called an AIDS-defining condition.
AIDS-defining conditions are certain cancers and illnesses called opportunistic infections.
Stage : Clinical Latency

If the infection goes undiagnosed or untreated, the immune system can bring the HIV level down some, but it cant completely control or contain it the virus is still active but multiplies more slowly, often without causing any symptoms. This is also called the clinical latency stage, or chronic HIV infection, and it can last up to 15 years.
Don’t Miss: Lil Wayne Hiv Rumors
Favorite Hiv Home Testing Resources
Need to take an STD test, but dont want to leave your home? myLab Box offers kits that screen for STDs like HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhea, HPV, and more. Depending on the test, youll mail in a small sample of urine, a vaginal swab, or a prick of blood, and youll get your results in one to five days.
Testing couldnt be any more convenient. This in-home HIV test is approved by the FDA and doesnt require sending a sample to a lab. You can test yourself in the privacy of your own home with an oral swab. The kit gives you a result in 20 to 40 minutes.
What Are The Six Factors That Progresses Hiv
The most important factor that affects HIV progression is the ability to achieve viral suppression. A variety of factors affect HIV progression and some people progress through the phases of HIV more quickly than others. Factors that affect HIV progression include:
Some factors can delay or slow the progression of HIV. These include:
- Taking care of ones health, including trying to lessen stress, having sex with condoms, and sleeping regularly
- Stopping the use of substances such as methamphetamine, ethanol, or cocaine
- Seeing a healthcare provider, as recommended, for HIV treatments
- Taking antiretroviral medications and achieving viral suppression
Read Also: Does Nba Youngboy Have An Std
Preventing Transmission By Blood Transfusions And Organ Transplants
In the United States, the following have almost eliminated transmission of HIV infection by organ transplantation or blood transfusion:
-
Screening donors of organs or blood for risk factors for HIV infection
-
Screening donated blood for HIV
Risk is reduced further by asking people with risk factors for HIV infection, regardless of their test results for HIV, not to donate blood or organs for transplantation.
However, developing countries have not consistently used sensitive HIV screening tests and have not restricted donors. Consequently, transmission by these routes is still a problem in these countries.
How Are Hiv And Aids Treated
Medicines can help people with HIV stay healthy. They can also prevent HIV from progressing to AIDS.
Health care providers prescribe a combination of different medicines for people with HIV and AIDS. They must be taken exactly as prescribed or they won’t work. These medicines:
- help keep the number of CD4 cells high
- reduce the viral load of HIV
Regular blood tests will check the number of CD4 cells in the body and the viral load.
If an HIV-positive person’s CD4 count gets low, doctors prescribe daily antibiotics. This prevents pneumocystis pneumonia, which happens in people with weakened immune systems.
Also Check: How To Find Out If Someone Has Hiv Aids
How Is Hiv Transmitted
HIV is transmitted when HIV-infected blood, sexual bodily fluids or breast milk enters another person’s bloodstream. This occurs most common during unprotected sex or intravenous drug use, when needles or other injecting equipment are shared.
HIV is mainly spread in three ways:
HIV is rarely transmitted in the following ways:
- Blood transfusions and organ transplants: The risk of HIV from a blood transfusion is extremely low today, with estimates ranging from 1 in 200,000 to 1 in 2,000,000 transfusions. The risk of HIV from an organ transplant is comparable. Accepted donors and their blood are thoroughly tested to rule out HIV and other blood-borne germs.
- Healthcare settings: As a result of needlestick accidents and other significant blood exposures, there is a very small, but real, risk of healthcare workers contracting HIV from patients. The risk of patients contracting an infection from healthcare workers is extremely low.
- Casual contact: HIV is not transmitted through casual contact. Outside the body, it dies quickly and is easily killed by soap and disinfectants such as bleach. There is no risk of HIV infection due to the following:
Donating blood
Respiratory And Cardiovascular Systems
HIV makes it hard to fight off respiratory problems such as the common cold and flu. In turn, an HIV-positive person may develop related infections, such as pneumonia.
Without treatment for HIV, advanced disease puts an HIV-positive person at an even greater risk for infectious complications, such as tuberculosis and a fungal infection called pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia .
PJP causes trouble breathing, cough, and fever.
The risk of lung cancer also increases with HIV. This is due to weakened lungs from numerous respiratory issues related to a weakened immune system.
According to available research , lung cancer is more prevalent among people with HIV compared to people without it.
People with HIV are more likely to develop high blood pressure. HIV also raises the risk of pulmonary arterial hypertension . PAH is a type of high blood pressure in the arteries that supply blood to the lungs. Over time, PAH will strain the heart and can lead to heart failure.
If a person has HIV with a low CD4 count, theyre also more susceptible to tuberculosis .
TB is an airborne bacterium that affects the lungs. Its a leading cause of death in people who have AIDS. Symptoms include chest pain and a bad cough that may contain blood or phlegm. The cough can linger for months.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Cause Hair Loss
What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Hiv And Aids
When first infected with HIV, a person may have:
- fever
- increased number of infections
- infections that are more severe than is typical
Without treatment, HIV can lead to a very weakened immune system and progress to AIDS. Illnesses that happen in AIDS are called “AIDS-defining conditions.”
AIDS-defining conditions include:
- very fast and severe weight loss
- a lung infection called pneumocystis pneumonia
- Kaposi sarcoma
- lymphoma
Prevalence And Incidence Of Blood
Prior to the introduction of compulsory testing for HIV antibodies in May and October 1985, about 1,380 haemophiliacs and about 200 transfusion recipients were infected in Germany with HIV by blood donations and plasma derivatives . With the introduction of antibody screening tests and obligatory virus inactivation procedures in the production process of plasma derivatives, the number of HIV and hepatitis virus infections by transfusion declined significantly, especially in the first 2 years. Since 2004, HIV antibody testing and HIV NAT further reduced the potential HIV burden of the source material . Since 1990/1991 no HIV infections have been transmitted by plasma derivatives .
According to reports to the Paul Ehrlich Institute, 2 HIV transmissions by cellular blood components have occurred after the introduction of NAT screening in 2004 . Both transmissions were due to very recent infections and a failure of the NAT systems used. In the case of 2007, presumably a low viral load and mutations in the primer binding region were responsible for the false-negative test results . Regarding the transmission reported in 2009, the HIV-positive donor sample was repeatedly tested negative with the NAT system used .
As recommended for HIV-infected donors, plasma and lymphocytes of the HIV-infected recipient should also be stored in order to possibly clarify the origin of infection and the transmission using molecular methods .
You May Like: Catching Hiv Early