Laboratory Methods For Diagnosis Of Hiv Infection In Infants And Children
The definitive diagnosis of HIV infection at any age requires diagnostic testing that confirms the presence of HIV. Serological testing identifies HIV antigen and/or antibody generated as part of the immune response to infection with HIV. In children older than 18 months of age, serological testing should be used in the same manner as in adults. However, maternal HIV antibody is transferred to the baby passively during pregnancy and then declines . Infected infants then go on to produce HIV antibody however, most commonly used HIV serological assays cannot distinguish between maternal HIV antibody and HIV antibody produced by the infant, making the interpretation of reactive HIV serological test results difficult . In order to diagnose HIV infection definitely in children aged less than 18 months, assays are required that detect the virus or its components . A range of laboratory-based techniques are available, and these are discussed in more detail in the following section.
What Are The Different Types Of Hiv Testing
There are three main types of HIV tests: antibody tests, RNA tests, and a combination test that detects both antibodies and viral protein called p24 . All tests are designed to detect HIV-1, which is the type of HIV in the United States. Some antibody tests and the combination test can also detect HIV-2 infections, which are usually limited to West Africa. No test is perfect tests may be falsely positive or falsely negative or impossible to interpret .
Positive test results are reportable to the health department in all 50 states and include the patient’s name. This information is then reported to the CDC so that the epidemiology and infection spread rates can be monitored. The names sent to the state remain confidential and will not be reported to employers, family members, or other such people. Some states allow anonymous testing in which the patient’s name is not recorded.
HIV antibody tests: HIV possesses many unique proteins on its surface and inside the virus itself. When someone is infected with HIV, their body produces proteins designed to tag the virus for elimination by the immune system. These proteins are called antibodies, and they are directed against the unique proteins of HIV. Unfortunately, these HIV antibodies do not eliminate the virus, but their presence serves as a marker to show that someone is infected with HIV. HIV antibody tests are the most commonly used tests to determine if someone has HIV.
What To Expect After Blood Tests
Once the needle is withdrawn, you’ll be asked to apply gentle pressure with a piece of gauze or bandage to the place where the needle was inserted. This helps stop bleeding. It also helps prevent swelling and bruising.
Most of the time, you can remove the pressure after a minute or two. You may want to keep a bandage on for a few hours.
Usually, you don’t need to do anything else after a blood test. Results can take anywhere from a few minutes to a few weeks to come back. Your doctor should get the results. It’s important that you follow up with your doctor to discuss your test results.
Read Also: Can You Get Hiv Through Saliva
What Do Blood Tests Show
Blood tests show whether the levels of different substances in your blood fall within a normal range.
For many blood substances, the normal range is the range of levels seen in 95 percent of healthy people in a certain group. For many tests, normal ranges vary depending on your age, gender, race, and other factors.
Your blood test results may fall outside the normal range for many reasons. Abnormal results might be a sign of a disorder or disease. Other factorssuch as diet, menstrual cycle, physical activity level, alcohol intake, and medicines also can cause abnormal results.
Your doctor should discuss any unusual or abnormal blood test results with you. These results may or may not suggest a health problem.
Many diseases and medical problems can’t be diagnosed with blood tests alone. However, blood tests can help you and your doctor learn more about your health. Blood tests also can help find potential problems early, when treatments or lifestyle changes may work best.
What Happens During The Test
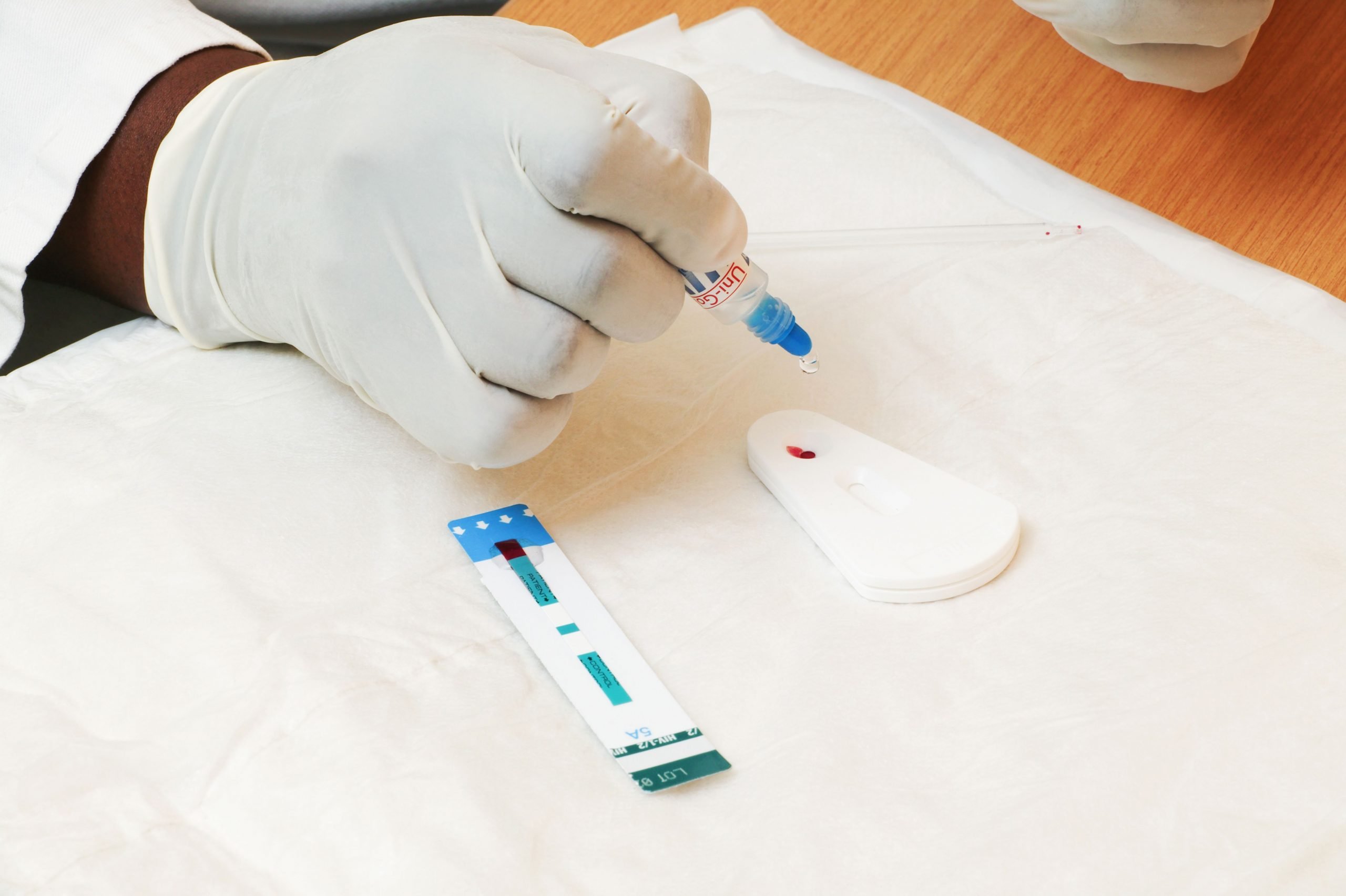
Before the test, a healthcare provider will explain the procedure. The person having the test will probably need to sign a consent form.
To help prevent any problems during the test, the person should be sure to tell the healthcare provider if:
- theyve had trouble giving blood in the past
- they have a bleeding disorder, such as hemophilia
- theyre taking anticoagulant medications
Recommended Reading: How Much To Get Hiv Test
Normal May Differ Between Men And Women
If you compare your blood test results with those of someone of the opposite sex, you may be surprised to find differences. For example, the normal reference range for the number of red blood cells in a complete blood count is between 5 million and 6 million cells per microliter for a man, but for women, its between 4 million and 5 million, according to the NHLBI.
Blood Tests To Assess Heart Disease Risk
A lipoprotein panel is a blood test that can help show whether you’re at risk for . This test looks at substances in your blood that carry cholesterol.
A lipoprotein panel gives information about your:
- Total cholesterol.
- LDL cholesterol. This is the main source of cholesterol buildup and blockages in the arteries.
- HDL cholesterol. This type of cholesterol helps decrease blockages in the arteries.
- Triglycerides. Triglycerides are a type of fat in your blood.
A lipoprotein panel measures the levels of LDL and HDL cholesterol and triglycerides in your blood. Abnormal cholesterol and triglyceride levels may be signs of increased risk for CHD.
Most people will need to fast for 9 to 12 hours before a lipoprotein panel.
Don’t Miss: Which Is The Main Goal Of Hiv Treatment Brainly
What Do The Test Results Mean
If a person tests positive for HIV on the ELISA test, they might have HIV. However, there can be false positives with the ELISA test. This means that test results indicate that the person has HIV when they actually do not. For example, having certain conditions such as Lyme disease, syphilis, or lupus may produce a false positive for HIV in an ELISA test.
For this reason, after a positive ELISA test, more sophisticated tests are done to confirm whether the person has HIV. These tests include the differentiation assay and a test called the nucleic acid test . If the person tests positive for HIV with either one of these tests, they probably have HIV.
Sometimes, HIV doesnt show up on the ELISA test even though a person has an HIV infection. This can happen if someone is in the early stages of the infection, and their body hasnt produced enough antibodies for the tests to detect. This early stage of HIV infection, in which a person has HIV but tests negative for it, is known as the window period.
According to the
What Is The Treatment For Hiv
The treatment for human immunodeficiency virus involves a combination of medications known as antiretroviral therapy . ART cannot cure HIV however, it can increase the survival rate of patients.
ART halts the multiplication of the virus and reduces the amount of virus in the body to help the patient stay healthier.
Once the treatment has been started, the patient must remain compliant with the dosage for the medicines to be effective. Noncompliance can result in developing resistance to the medicines.
Recommended Reading: How To Reduce The Risk Of Hiv
What Is It Used For
An HIV test is used to find out if you have been infected with HIV. HIV is the virus that causes AIDS . Most people with HIV don’t have AIDS. People with AIDS have an extremely low number of immune cells and are at risk for life-threatening illnesses, including dangerous infections, a severe type of pneumonia, and certain cancers, including Kaposi sarcoma.
If HIV is found early, you can get medicines to protect your immune system. HIV medicines may prevent you from getting AIDS.
What Is The 4th Generation Hiv Test
The fourth generation HIV test, also called an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay test, is a more complete screening that can identify acute HIV. This is the time when the virus is multiplying rapidly and youre more likely to pass the infection.
In the first few weeks after exposure to HIV, your body produces an antigen known as p24. This protein is only present in people who have acute HIV infection. It triggers your immune system to respond.
The fourth generation tests can identify both HIV-specific antigen p24 and HIV antibodies with a blood sample.
The fourth generation tests require a blood sample thats sent to a lab for testing. Blood testing done by a lab is the most accurate type of test.
There are many products approved for fourth generation testing, including:
- ADVIA Centaur HIV Ag/Ab Combo Assay
- Elecsys HIV Combi PT
- Genscreen ULTRA HIV Ag-Ab
- VITROS HIV Combo Test
The healthcare clinic or doctors office you visit for an HIV test can tell you more about the exact test they use.
tests that can test for the presence of HIV. HIV testing can be done by drawing blood from a vein, a finger stick, or taking an oral swab of fluid.
Tests can measure antibodies, antigen/antibody , and theres also a nucleic acid test . The NAT test can identify HIV and viral load . It can tell if you have HIV within around 10 to 33 days of exposure.
Older tests like the third generation tests arent reliable until about 3 months after exposure to the virus.
You May Like: What Are The Current Treatments For Hiv
Viral Load And Cd4 Levels
When someone contracts HIV, the virus begins to take over specific cells in the immune system, called CD4 cells.
When the CD4 cells replicate, the HIV cells inside them also replicate. HIV hijacks the cellular machinery of CD4 cells to reproduce and shed more HIV, which means the viral load increases.
As the HIV viral load increases, the number of healthy CD4 cells decreases as they are destroyed creating HIV copies.
Treatment aims to produce a low viral load and a high CD4 count. When a person has achieved this, their HIV is well controlled.
A low or undetectable viral load means the virus is not progressing. It also means that HIV is not attacking the immune system as actively. This gives the immune system the chance to rebuild its healthy cell count. As a result, the number of CD4 cells in the persons body will increase as their viral falls.
A doctor will usually test a persons viral levels when they first diagnose HIV. Doctors will recommend an HIV test if someone presents symptoms of HIV or if they may have come into contact with the virus.
People living with HIV will have repeat viral load tests throughout their lives to monitor the condition. They should get tested once every 3 to 4 months during treatment.
Additionally, a person should get tested due to any alteration in their medication or if their symptoms change.
What Is A False Positive Test
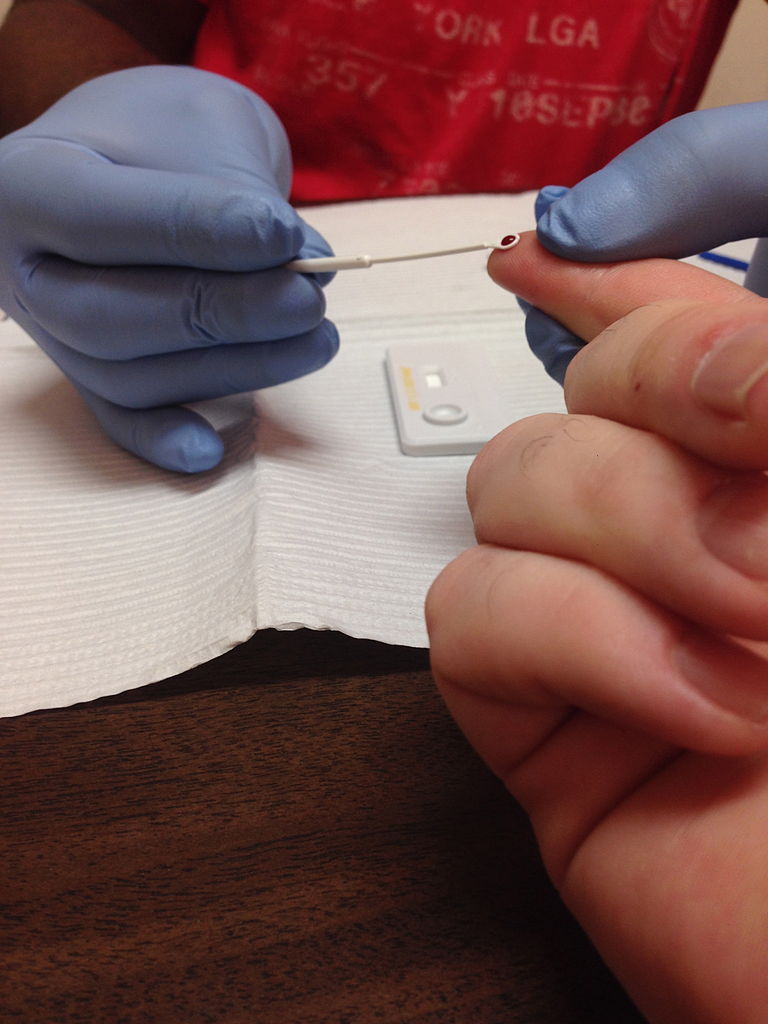
You can get a false positive HIV test. This is when a person who doesnt have HIV tests positive.
Newer tests like the fourth generation test are more accurate, but false positive and false negative results can happen for many reasons.
False positive results can happen if:
- the testing sample is contaminated
- the lab misreads or mislabels the test
- youve been part of a HIV vaccine study
Keep in mind, testing blood versus saliva may also affect accuracy of results.
If you receive a positive result, your doctor or clinic where you were tested will recommend a second test to confirm results. This will guide next steps in the process.
There are many options to get tested for HIV with the fourth generation test, including free clinics.
Some options include:
- sexual health clinic
- community health center
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website has a search tool to locate the nearest testing site by zip code.
Generally, there are no risks to the fourth generation test. Its exactly like any normal blood work or testing done by your healthcare provider during regular checkups.
Occasionally, there may be rare complications:
Let your healthcare provider know if youre afraid of needles and if you have any blood disorders that might increase your risk when blood is drawn. If you have any problems after the blood draw, contact the medical office where the test was done.
Read Also: Which Body Fluids Transmit Hiv
Can I Take The Test At Home
At-home HIV tests are a convenient way to take an HIV test in a private location. Testing for HIV at home is a form of HIV screening that requires additional follow-up if preliminary results are positive. At-home HIV tests can be obtained online, at a pharmacy, or at health departments and community-based organizations.
Why Test For Hiv
Having an HIV test and knowing your test result will help you to make decisions about your health. If HIV is diagnosed early, antiretroviral therapy can slow or stop the damage to the immune system.
HIV testing guidelines in B.C. recommend that everyone aged 18 to 70 years has an HIV test every 5 years. They recommend more frequent testing for people who:
- belong to populations that have a greater chance of acquiring HIV
- are pregnant
- experience a change in their health that suggests HIV and
- request a test.
It is your choice to have an HIV test. Talk to your health care provider if you have any concerns or questions about the HIV test or your HIV test result.
Don’t Miss: How To Live With Someone With Hiv
Why Do I Need An Immunoglobulins Blood Test
You may need this test if your health care provider thinks your immunoglobulin levels might be too low or too high.
Symptoms of levels that are too low include:
- Frequent and/or unusual bacterial or viral infections
- Lung infections
- Family history of immunodeficiency
If your immunoglobulin levels are too high, it may be a sign of an autoimmune disease, a chronic illness, an infection, or a type of cancer. Symptoms of these conditions vary greatly. Your health care provider may use information from your physical exam, medical history, and/or other tests to see if you are at risk for one of these diseases.
Why Do Some Blood Tests Require Fasting
Everything you eat and drink contains vitamins, proteins, and other nutrients that can cause the related levels in your blood to temporarily spike or drop.
Fasting for 812 hours helps ensure that blood test results are free from these variables, making your test results as accurate as possible.
Some common tests that may require fasting include:
- cholesterol tests
Results may take anywhere from a few hours to a few days to become available. Heres an overview of how long some common tests may take:
- complete blood count : 24 hours
- basic metabolic panel: 24 hours
- complete metabolic panel: 2472 hours
- lipid panel: 24 hours.
This can depend on the specific lab where you get tested or how many tests you get done at once. If you order multiple tests, you may not get the complete results until all of the tests are completed.
Sometimes a lab will only release results to your doctor, who reviews them and then releases them to you.
Don’t Miss: What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
White Blood Cell Count
White blood cells are a subset of cells produced in bone marrow whose primary role is to fight infection. A white blood cell count is one of the panel of tests included in the CBC that measures not only the total number of leukocytes but also the different types of white blood cells in a blood sample, namely:
Within the context of HIV, an elevated WBC typically means that your body is fighting an infection. Other tests can then be performed to pinpoint the cause.
An elevation of certain white blood cells may indicate a specific type of infection or an allergic inflammatory response. For example, higher than normal eosinophils may suggest a parasitic infection like toxoplasmosis, while elevated basophils can develop in people with a hypersensitive drug reaction.
A decrease in white blood cells may be the result of HIV medications , a minor viral infection, or a major opportunistic infection like tuberculosis.
CD4 T-cell lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that HIV preferentially targets and infects. For this reason, they serve as the primary marker of your immune status if you have HIV.
Test Values Can Be Different From Lab To Lab
Lab technicians reports compare your blood test results with a range that is considered normal for that laboratory. The labs reference range is based on test results from many people previously tested in that lab. This normal range may not be the same as another labs, notes the Food and Drug Administration, so dont be surprised if you find that a prior blood test report varies from newer reports the difference could be in the lab.
Don’t Miss: Can Hiv Be Cured Early
Normal May Or May Not Vary By Age
For some tests, such as the hemoglobin test, normal results vary by age. For children, for example, a hemoglobin level of about 11 to 13 grams/deciliter is normal, while for men, a value of about 14 to 17 g/dl is normal, and for women, 12 to 15 g/dl is normal. But for other tests, such as LDL cholesterol, a level less than 100 milligrams/deciliter is considered optimal regardless of age. That being said, your age and other risk factors for heart disease may influence how your doctor reacts if your blood test shows a higher-than-optimal LDL cholesterol level. If you are a man over 45 or a woman over 55 and you have heart disease or diabetes, your doctor will likely advise you to take steps to lower your LDL cholesterol if it is higher than 100 mg/dl.