Lack Of Symptoms In Early Stages
ARS is common once a person has HIV. Still, this isnt the case for everyone. Some people have HIV for years before they know they have it. According to HIV.gov, symptoms of HIV may not appear for a decade or longer. This doesnt mean that cases of HIV without symptoms are less serious. Also, a person who doesnt experience symptoms could still transmit HIV to others.
Symptoms in early HIV tend to appear if the rate of cell destruction is high. Not having symptoms can mean that not as many CD4 cells, a type of white blood cell, are killed early on in the disease. Even though a person has no symptoms, they still have the virus. Thats why regular HIV testing is critical to prevent transmission. Its also important to understand the difference between a CD4 count and a viral load.
Seroconversion And Acute Hiv Infection
In the first few weeks after infection with HIV, some people have a short flu-like illness that is called a seroconversion illness. This coincides with the period during which the body first produces antibodies to HIV. The most commonly experienced symptoms are fever, swollen glands, muscle aches and tiredness.
The severity of symptoms at this stage can vary considerably between people they can be so mild as to go unnoticed, or so severe that admission to hospital is needed. They usually go away within two to three weeks.
This early stage of HIV infection is called acute HIV infection. The US public health agency the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention describes it as stage 0.
During acute infection, there are very high levels of HIV in the body , which means that the risk of passing HIV on is higher than at other times.
You can start HIV treatment during acute infection. HIV treatment lowers the amount of virus in the body, which allows the immune system to strengthen and helps prevent illnesses from occurring. Starting HIV treatment in this early phase may have particular benefits in terms of preserving the immune system.
People who start HIV treatment go straight to the chronic stage of infection, described towards the end of the page.
Stage : Symptomatic Stage
The immune systembecomes seriously damaged by HIV over the years. The lymph nodes and tissuesare damaged or destroyed. The body cannot continue to replace the lost T-helpercells as the HIV infection becomes stronger and more varied.
Symptoms develop as the immune systemfails, and may include weight loss, chronic diarrhoea, night sweats and fever.The symptoms worsen as the immune system starts to slow down. This is the timewhen infections known as opportunistic infections and cancers can occur.
You May Like: Can You Get Hiv Oral Sex
Stage : Clinical Latent Hiv Infection
This phase begins after the acute symptoms have resolved and the only indication of infection may be mild swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck.
This can be a tricky time because, despite the lack of obvious illness, the HIV virus is still active, damaging and destroying cells in the immune system. Without treatment, the clinical latent phase of HIV can last for around 10 years, during which the infected person can easily pass the virus along to someone else even if they’re experiencing no symptoms whatsoever.
Stage : Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome

This stage is widely known to be the most serious of the three. The immune system of those with AIDs becomes completely weakened, and they become at risk of experiencing a number of illnesses referred to as opportunistic infections – although these arent as common now with the advancement in medical treatments surrounding HIV and AIDs .
See also:HIV and Aids: Myths and Facts
Read Also: Is Hiv Transmitted Through Oral Sex
How Long Does It Take Hiv To Turn Into Aids
If a person with HIV goes undiagnosed and without treatment, its possible for the virus to continue to develop into the next stages. According to Mayo Clinic, it can take around 8-10 years for HIV to develop into AIDS without the appropriate treatment .
It is now not as common for HIV to progress into AIDS with early diagnosis and prompt testing to thank for allowing people with HIV to live long and happy lives.
Stage : Clinical Latency
In this stage, the virus still multiplies, but at very low levels. People in this stage may not feel sick or have any symptoms. This stage is also called chronic HIV infection.
Without HIV treatment, people can stay in this stage for 10 or 15 years, but some move through this stage faster.
If you take HIV medicine every day, exactly as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load, you can protect your health and have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to your sexual partner.
But if your viral load is detectable, you can transmit HIV during this stage, even when you have no symptoms. Its important to see your health care provider regularly to get your viral load checked.
Also Check: What Kind Of Infection Is Hiv
What Are The Symptoms Of Hiv
Not everyone will have identical symptoms because it depends on the person and what stage of the disease they are in.
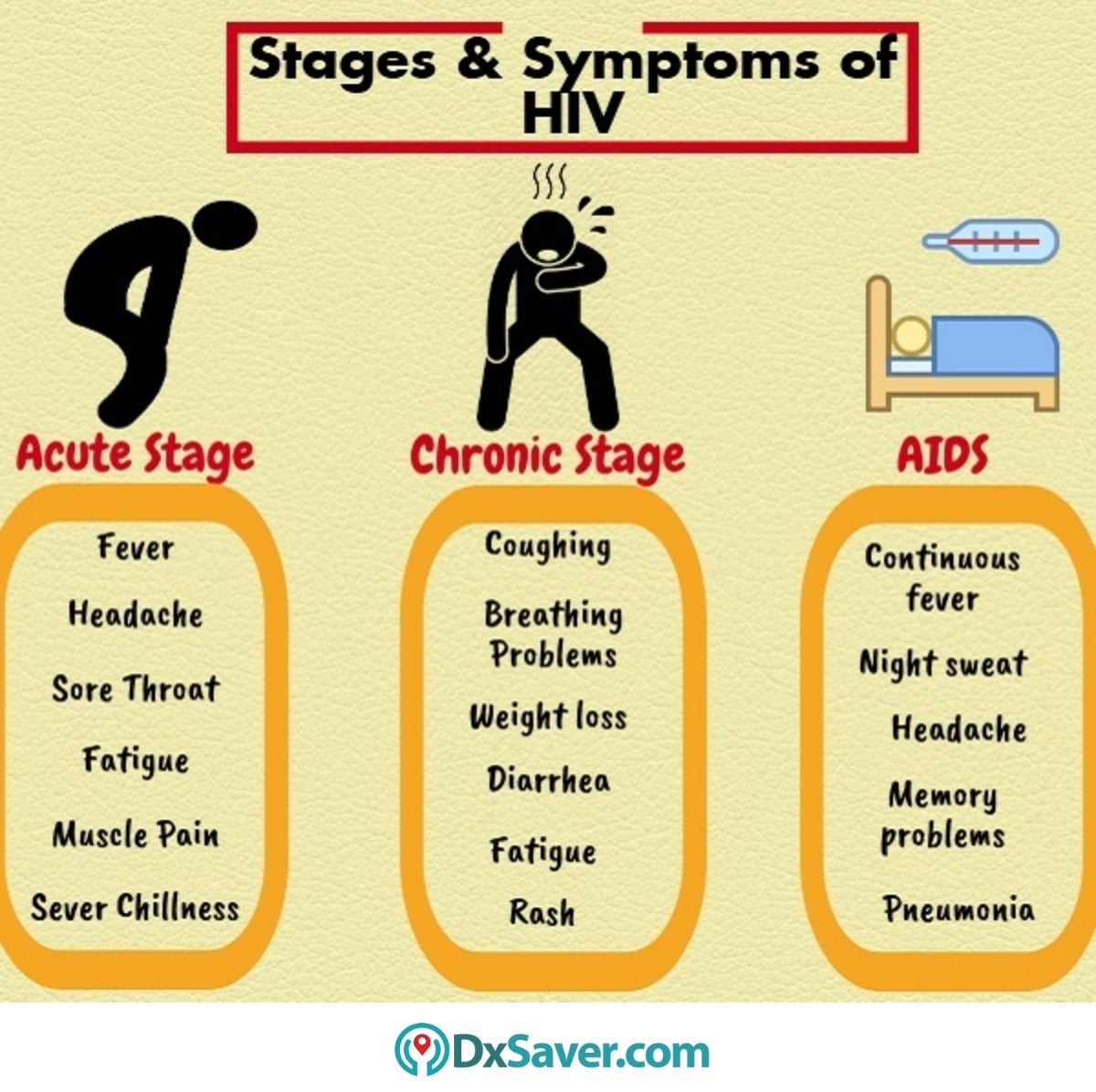
There are three stages of human immunodeficiency virus . Each stage has a unique set of symptoms. These include the following
Stage 1: Acute HIV infection
This stage starts around two to four weeks after getting HIV. The symptoms are similar to those of the flu, which last for a week or two. Symptoms include the following
Three Stages Of Hiv Infection
HIV infection takes its toll in three stages. Unless you take medication, the infection will worsen over time. Eventually, it will overwhelm your immune system. Below we will discuss in detail the stages of HIV.
1. Acute HIV Infection
A short time after infection with HIV, the symptoms may become evident. At this point, your immune system is fighting the virus, similar to the flu. This typically sets in within two to six weeks after the virus has been acquired. This period is called primary HIV infection or acute retroviral syndrome.
The symptoms are often like the flu, lasting a week then disappearing. They include:
- A headache
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Red rash on the torso
If you act quickly, you can prevent HIV from escalating to AIDS. Anti-HIV drugs called PEP can be very effective after having unprotected sex with someone who is HIV-positive. However, it is critical to start taking the drugs within 72 hours of exposure.
2. Chronic HIV Infection
As your immune system becomes overwhelmed with the HIV virus, the flu-like symptoms will disappear. Doctors describe this as the asymptomatic or clinical latent period. During this time, you wont have any symptoms of HIV. You may not realize youre infected with HIV.
You can easily transmit HIV to other people. This symptom-less stage can last up to 10 years or more.
If you’re taking medications and have adopted a healthy lifestyle, your HIV infection may not worsen.
3. AIDS
Don’t Miss: Is It Hard To Get Hiv
What Is The Connection Between The Hiv Life Cycle And Hiv Medicines
Antiretroviral therapy is the use of HIV medicines to treat HIV infection. People on ART take a combination of HIV medicines every day. HIV medicines protect the immune system by blocking HIV at different stages of the HIV life cycle.
HIV medicines are grouped into different drug classes according to how they fight HIV. Each class of drugs is designed to target a specific step in the HIV life cycle.
Because an HIV regimen includes HIV medicines from at least two different HIV drug classes, ART is very effective at preventing HIV from multiplying. Having less HIV in the body protects the immune system and prevents HIV from advancing to AIDS.
ART cant cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission .
Early Symptoms In Primary Hiv
The first noticeable stage is primary HIV infection. This stage is also called acute retroviral syndrome , or acute HIV infection. Because HIV infection at this stage usually causes flu-like symptoms, its possible for someone in this stage to think their symptoms are due to a severe flu rather than HIV. Fever is the most common symptom.
Other symptoms include:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention , primary HIV symptoms may show up two to four weeks after initial exposure. Symptoms can continue for up to several weeks. However, some people may exhibit the symptoms only for a few days.
People with early HIV sometimes dont show any symptoms, yet they can still transmit the virus to others. This is attributed to the fast, unrestrained viral replication that occurs in the early weeks after contracting the virus.
Read Also: What Treatment Is Used For Hiv
What Are The Four Stages Of Hiv
The World Health Organization classifies human immunodeficiency virus into four stages
- Stage 1 : The CD4+ cell count is at least 500 cells per microliter.
- Stage 2 : The CD4+ cell count is 350 to 499.
- Stage 3 : The CD4+ cell count is 200 to 349.
- Stage 4 : The CD4+ cell count is less than 200.
The normal CD4+ cell count should be between 500 and 1600 cells per microliter. The higher the CD4+ cell count, the lower the chances of opportunistic diseases.
Third Stage: Aids Symptoms
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV infection. This is usually when your CD4 T-cell number drops below 200 and your immune system is badly damaged. You might get an opportunistic infection, an illness that happens more often and is worse in people who have weakened immune systems. Some of these, such as Kaposi’s sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia , are also considered âAIDS-defining illnesses.â
If you didn’t know earlier that you were infected with HIV, you may realize it after you have some of these symptoms:
- Being tired all the time
- Swollen lymph nodes in your neck or groin
- Fever that lasts more than 10 days
Don’t Miss: How Long Do You Live With Hiv
How Is Hiv Transmitted
Human immunodeficiency virus is transmitted by coming in direct contact with certain body fluids of the person infected with HIV. These fluids are as follows
- Blood
- Receiving blood products that are contaminated with HIV
- Getting stuck with an HIV-contaminated needle
Hence, taking precautions either while having sex or sharing a needle is the best way to prevent HIV.
Howcan I Test For Hiv
It is entirely yourchoice whether you test for HIV on its own, or as part of a screen in combination with othersexually transmitted infections . Testing for several STIs provides amore complete view of your current sexual health.
Better2Know providesvarious HIV tests which can be taken at different times, depending on how longhas passed after your last incident of concern.
Our HIV testingoptions include:
- 28-Day HIV DUO Test this test is extremelyaccurate at 28 days and is recommended by the UKs HIV testing guidelines.
- 28-Day 5th Generation HIVTest thisadvanced test distinguishes between the three markers of HIV and will tell you which you have tested positive for.
- 10-Day HIV RNA PCR Test this test can be taken 10days after an incident of concern, providing the earliest possible indicationof an HIV infection.
- Instant HIV Test available at 26 days, thistest will provide results within 20 minutes at your appointment.
You may decide to testfor HIV as part of a Better2Know screen, in combination with other STIs.Testing for several infections, our screens are designed to provide total peaceof mind surrounding your sexual health.
Our HIV screeningoptions include:
Recommended Reading: Can Someone Hiv Positive Become Hiv Negative
Signs And Symptoms Of Hiv
Within two to four weeks after infection, its possible for people with HIV to experience flu-like symptoms. Symptoms may include fever, chills, rash, night sweats, and sore throat. This is the first stage of HIV and is referred to as acute HIV infection.
Some of the other symptoms of HIV infection may include:
- Muscle aches
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Mouth ulcers
Symptoms can vary from person to person. Its also possible for people to not feel sick at all after getting infected. The longer someone goes untreated, the higher the likelihood the infection will progress to a later stage.
- Related
Latency Causes A Break In Symptoms
After initial exposure and possible primary infection, HIV may transition into a stage called clinically latent infection. Its also referred to as asymptomatic HIV infection due to a noticeable lack of symptoms. This lack of symptoms includes possible chronic symptoms.
According to HIV.gov, latency in HIV infection can last for 10 or 15 years. This doesnt mean that HIV is gone, nor does it mean that the virus cant be transmitted to others. Clinically latent infection may progress to the third and final stage of HIV, also referred to as AIDS.
The risk for progression is higher if a person with HIV isnt receiving treatment, such as antiretroviral therapy. Its important to take prescribed medications during all stages of HIV even if there arent any noticeable symptoms. There are several medications used for HIV treatment.
Also Check: How Soon Can Hiv Be Detected
How Long Does It Take For Hiv To Infect The Body
On average it takes 2 to 12 weeks after infection for the virus to take hold and for the body to start to mount its defence by developing antibodies. From the point of exposure, if any transmission took place, the person is said to have HIV. 72 hours after any possible exposure, a tablet can be taken that can prevent the onward transmission, if a person thinks they have recently been at risk, they can take the pill to prevent infection.
Clinical Latency Stage Of Hiv Infection
The symptoms during ARS may last for a few weeks, according to the National Institutes of Health.
After this point, the infection progresses to the clinical latency stage, a period during which the virus reproduces at very low levels, but it is still active.
Also known as asymptomatic HIV infection or chronic HIV infection, the clinical latency stage typically causes no HIV-related symptoms.
For people who are not taking any anti-retroviral medication for their infection, the clinical latency stage lasts for 10 years, on average, but it may progress quicker.
ART, though, can keep the virus from growing and multiplying, prolonging the clinical latency state for several decades.
It’s important to note that people living with HIV in the clinical latency stage are contagious and can still transmit the virus to other people. But, as the CDC notes, people who take ART exactly as prescribed and maintain an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of transmitting HIV to their HIV negative-partner through sex.
Also Check: Does Hiv Medication Make You Gain Weight
Understanding The Stages Of Hiv
The human immunodeficiency virus is the cause of the potentially life-threatening chronic condition known as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome .
The HIV virus damages your immune system, which affects your body’s ability to fight the disease.
HIV is a sexually transmitted infection that can be spread with contact with infected blood. The virus can also be spread from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding.
Unless you take medication, there may be several years delay before HIV damages your immune system to progress to AIDS.
There is no cure for HIV/AIDS, but with medication, you can greatly low the progress to AIDS and have significantly reduced the numbers of AIDS-related deaths.
Stages Of Hiv Infection

Stages of Infection
There are four stages of HIV and as with all illnesses, how it progresses, how long it takes and the affect it has on the individual depends on a number of factors for example, general health, lifestyle, diet etc.
Stage 1: Infection
HIV quickly replicates in the body after infection. Some people develop short lived flu-like symptoms for example, headaches, fever, sore throat and a rash within days to weeks after infection. During this time the immune system reacts to the virus by developing antibodies this is referred to as sero-conversion.
Stage 2:Asymptomatic
As the name suggests, this stage of HIV infection does not cause outward signs or symptoms. A person may look and feel well but HIV is continuing to weaken their immune system. This stage may last several years and without a HIV test many people do not know they are infected.
Stage 3:Symptomatic
Over time the immune system becomes damaged and weakened by HIV and symptoms develop. Initially they can be mild but they do worsen, symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, mouth ulcers, thrush and severe diarrhoea. The symptoms are caused by the emergence of opportunistic infections they are referred to as opportunistic infections because they take advantage of a persons weakened immune system. Some examples of opportunistic infections are PCP, toxoplasmosis, TB and kaposi sarcoma.
Stage 4:AIDS/Progression of HIV to AIDS
Don’t Miss: Can You Get Hiv Through Kissing
Stage : Primary Infection
This is the period when the virus first enters the body and the immune system begins to react. According to the United States Department of Health and Human Services , 40% to 90% of people will experience flu-like symptoms within two to four weeks of being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus as the body fights to control the infection.
Symptoms of acute HIV infection include:
- Fever
- Lymphadenopathy
- Mouth ulcers
Collectively, these symptoms are referred to as acute retroviral syndrome or, less often, acute seroconversion syndrome or seroconversion illness.
Some people with ARS also will experience nausea, diarrhea, or vomiting, and one in five will develop an “HIV rash,” a maculopapular skin condition characterized by raised, pink/red areas covered with small, pimple-like bumps that often merge together into one. HIV rash usually affects the upper body and sometimes is accompanied by ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth or genitals. Outbreaks usually resolve within one to two weeks.