What Is Hiv What Is Aids
HIV is a virus that attacks the immune system, the body’s natural defence system. Without a strong immune system, the body has trouble fighting off disease. Both the virus and the infection it causes are called HIV.
White blood cells are an important part of the immune system. HIV infects and destroys certain white blood cells called CD4+ cells. If too many CD4+ cells are destroyed, the body can no longer defend itself against infection.
The last stage of HIV infection is AIDS . People with AIDS have a low number of CD4+ cells and get infections or cancers that rarely occur in healthy people. These can be deadly.
But having HIV doesn’t mean you have AIDS. Even without treatment, it takes a long time for HIV to progress to AIDSusually 10 to 12 years.
When HIV is diagnosed before it becomes AIDS, medicines can slow or stop the damage to the immune system. If AIDS does develop, medicines can often help the immune system return to a healthier state.
With treatment, many people with HIV are able to live long and active lives.
There are two types of HIV:
- HIV-1, which causes almost all the cases of AIDS worldwide
- HIV-2, which causes an AIDS-like illness. HIV-2 infection is uncommon in North America.
Why Might People Infected With Hiv Have A Higher Risk Of Some Types Of Cancer
Infection with HIV weakens the immune system and reduces the body’s ability to fight viral infections that may lead to cancer . The viruses that are most likely to cause cancer in people with HIV are :
- Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus , also known as human herpesvirus 8 , which causes Kaposi sarcoma and some subtypes of lymphoma
more advanced at diagnosis, delays in cancer treatment, or poorer access to appropriate cancer treatment.
Preventive Treatment After Exposure
People who have been exposed to HIV from a blood splash, needlestick, or sexual contact may reduce the chance of infection by taking antiretroviral drugs for 4 weeks. These drugs are more effective when they are started as soon as possible after the exposure. Taking two or more drugs is currently recommended.
Doctors and the person who was exposed typically decide together whether to use these preventive drugs. They base the decision on the estimated risk of infection and the possible side effects of the drugs. If they do not know whether the source is infected with HIV, they consider how likely the source is to be infected. However, even when the source of the exposure is known to be infected with HIV, the risk of infection after exposure varies, depending on the type of exposure. For example, risk from a blood splash is less than that from a needlestick.
Immediately after exposure to HIV infection, what is done depends on the type of exposure:
-
If skin is exposed, it is cleaned with soap and water.
-
Puncture wounds are cleaned with antiseptic.
-
If mucous membranes are exposed, they are flushed with large amounts of water.
Also Check: Can You Get Hiv Without Having Sex
Can Hiv/aids Be Prevented
You can reduce the risk of spreading HIV by
- Getting tested for HIV
- Choosing less risky sexual behaviors. This includes limiting the number of sexual partners you have and using latex condoms every time you have sex. If your or your partner is allergic to latex, you can use polyurethane condoms.
- Getting tested and treated for sexually transmitted diseases
- Not injecting drugs
- Talking to your health care provider about medicines to prevent HIV:
- PrEP is for people who don’t already have HIV but are at very high risk of getting it. PrEP is daily medicine that can reduce this risk.
- PEP is for people who have possibly been exposed to HIV. It is only for emergency situations. PEP must be started within 72 hours after a possible exposure to HIV.
NIH: National Institutes of Health
What Can People Infected With Hiv Do To Reduce Their Risk Of Cancer Or To Find Cancer Early

Taking cART as indicated based on current HIV treatment guidelines lowers the risk of Kaposi sarcoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma and increases overall survival.
The risk of lung, oral, and other cancers can be reduced by quitting smoking. Because HIV-infected people have a higher risk of lung cancer, it is especially important that they do not smoke. Help with quitting smoking is available through the National Cancer Institutes smoking quitline at 18774487848 and other NCI resources, which are listed on the Tobacco page.
The higher incidence of liver cancer among HIV-infected people appears to be related to more frequent infection with hepatitis virus than among HIV-uninfected people . Therefore, HIV-infected individuals should know their hepatitis status.
In addition, if HIV-infected people currently have viral hepatitis, they should discuss with their health care provider whether antiviral treatment is an option for them . Some drugs may be used for both HBV-suppressing therapy and cART .
Because HIV-infected women have a higher risk of cervical cancer, it is important that they be screened regularly for this disease. In addition, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends vaccination against human papillomavirus for women and men with HIV infection up to age 26 years. Cervical cancer screening guidelines that incorporate results of a Pap test and an HPV DNA test are evolving, and women should discuss screening options with their healthcare provider .
Also Check: How Long Can Hiv Be Dormant
Make Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet to keep your immune system strong. A heart-healthy diet can help prevent some of the problems, such as high cholesterol, that can be caused by treatment for HIV.footnote 24
- Learn how to deal with the weight loss that HIV infection can cause.
- Learn how to handle food properly to avoid getting a foodborne illness. For more information, see the topic Foodborne Illness and Safe Food Handling.
- Exercise regularly to reduce stress and improve the quality of your life. Take steps to help prevent HIV-related fatigue.
- Don’t smoke. People with HIV are more likely to have a heart attack or get lung cancer.footnote 25, footnote 26 Cigarette smoking can raise these risks even more.
- Don’t use illegal drugs. And limit your use of alcohol.
A Sexually Transmitted Infection
Katie Salerno/Flickr Creative Commons
Contracting other sexually transmitted diseases can significantly increase the risk of getting HIV. For instance, some STDs like syphilis and herpes cause skin lesions that make it easier for HIV to enter the body.
STDs may also cause inflammation, which is something that is triggered by the body’s immune system. HIV preferentially infects defensive white blood cells, so when there are more of them around, it’s easier to contract HIV.
Having an STD like gonorrhea or syphilis means that you’ve engaged in unprotected sex, a key risk factor for HIV. So if you have been diagnosed with an STD, talk to your healthcare provider about how you can reduce your HIV risk.
Don’t Miss: What Does Hiv Non Reactive Mean
Diagnosis Of Hiv Infection
-
Tests to detect antibodies to the HIV virus in a sample of blood or saliva
-
Tests to detect HIV RNA in a sample of blood
Early diagnosis of HIV infection is important because it makes early treatment possible. Early treatment enables infected people to live longer, be healthier, and be less likely to transmit HIV to other people.
Doctors usually ask about risk factors for HIV infection Transmission of HIV Infection Human immunodeficiency virus infection is a viral infection that progressively destroys certain white blood cells and can cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome . HIV is transmitted… read more and about symptoms .
Doctors also do a complete physical examination to check for signs of opportunistic infections, such as swollen lymph nodes and white patches inside the mouth , and for signs of Kaposi sarcoma of the skin or mouth.
Hepatitis B And Hepatitis C
Hepatitis B and hepatitis C are also common among people living with HIV and can be treated. Both infections can be more common in people who have HIV and people who inject drugs. If left untreated, they can cause serious damage to the liver. Hepatitis C can be cured and chronic hepatitis B can be managed with treatment.
How can I prevent Hepatitis B and C?
Using a condom for sex and not sharing needles and other injecting equipment are some of the main ways to reduce your risk of getting or passing on hepatitis B and C.
A vaccine is available for hepatitis B. If you have HIV its recommended that you get the hepatitis B vaccine. People with HIV are also advised to regularly test for both hepatitis B and C. Its especially important that pregnant women are tested for hepatitis B, as without treatment, the infection can be passed on to babies during pregnancy.
Read Also: When Will Cure For Hiv Be Found
What’s The Relationship Between Drug Use And Viral Infections
People who engage in drug use or high-risk behaviors associated with drug use put themselves at risk for contracting or transmitting viral infections such as human immunodeficiency virus , acquired immune deficiency syndrome , or hepatitis. This is because viruses spread through blood or other body fluids. It happens primarily in two ways: when people inject drugs and share needles or other drug equipment and when drugs impair judgment and people have unprotected sex with an infected partner. This can happen with both men and women.
Drug use and addiction have been inseparably linked with HIV/AIDS since AIDS was first identified as a disease. According to the CDC, one in 10 HIV diagnoses occur among people who inject drugs.1 In 2016, injection drug use contributed to nearly 20 percent of recorded HIV cases among menmore than 150,000 patients. Among females, 21 percent of HIV cases were attributed to IDU.2 Additionally, women who become infected with a virus can pass it to their baby during pregnancy, regardless of their drug use. They can also pass HIV to the baby through breastmilk.
Testing For Drug Resistance
HIV often changes or mutates in the body. Sometimes these changes make the virus resistant to certain medicines. Then the medicine no longer works.
Medical experts recommend testing the blood of everyone diagnosed with HIV to look for this drug resistance.footnote 8 This information helps your doctor know what medicines to use.
You also may be tested for drug resistance when:
- You are ready to begin treatment.
- You’ve been having treatment and your viral load numbers stop going down.
- You’ve been having treatment and your viral load numbers become detectable after not being detectable.
Read Also: How To Not Get Hiv
Through Needles Or Other Instruments
Health care workers who are accidentally pricked with an HIV-contaminated needle have about a 1 in 300 chance of contracting HIV unless they are treated as soon as possible after exposure. Such treatment reduces the chance of infection to less than 1 in 1,500. The risk increases if the needle penetrates deeply or if the needle is hollow and contains HIV-contaminated blood rather than simply being coated with blood .
Infected fluid splashing into the mouth or eyes has less than a 1 in 1,000 chance of causing infection.
What Is Hiv And Aids
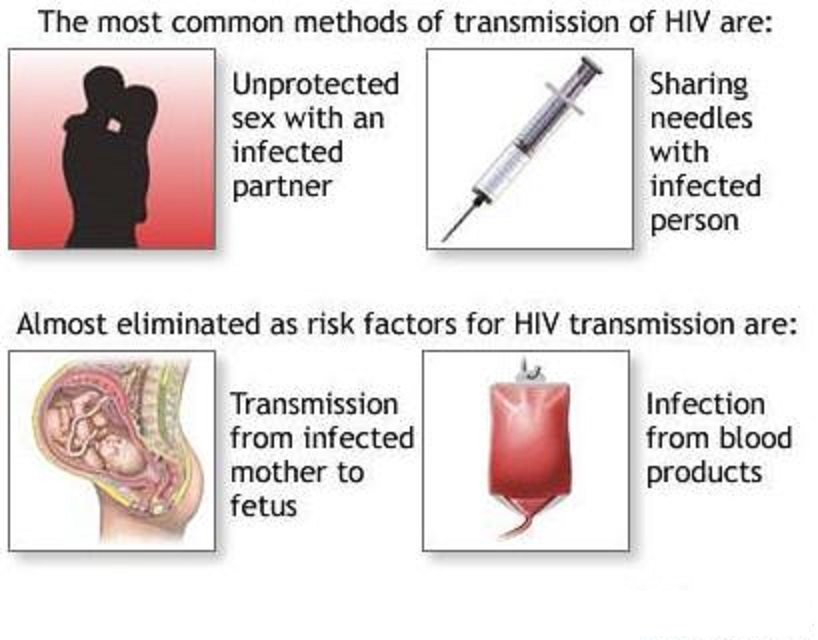
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency virus, which is the virus that causes HIV infection. The abbreviation HIV can refer to the virus or to HIV infection.
AIDS stands for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. AIDS is the most advanced stage of HIV infection.
HIV attacks and destroys the infection-fighting CD4 cells of the immune system. The loss of CD4 cells makes it difficult for the body to fight off infections and certain cancers. Without treatment, HIV can gradually destroy the immune system and HIV infection advances to AIDS.
Don’t Miss: What Can Be Done About Hiv Stigma
Are Women More Likely To Get Hiv
Yes. Biologically speaking, a woman is more vulnerable to heterosexual transmission of the disease because the genitalia are easily exposed to seminal fluids.
Gender inequality has great influence on the spread of HIV/AIDS among women. In some cultures, many women and girls are often put in situations where they engage in non-consensual sex or have sex for money.
In the U.S., minority communities have been hit the hardest by HIV. African American and Hispanic women together represent less than 25% of all U.S. women, yet they account for more than 78% of AIDS cases reported among women in the country.
If You Don’t Have A Doctor
Public health units and other organizations may provide free or low-cost, confidential testing and counselling about HIV and high-risk behaviour.
If you don’t have a doctor, contact one of the following for information on HIV testing in your area:
- Your local health unit
- CATIE: 1-800-263-1638 or online at www.catie.ca
You May Like: Why No Vaccine For Hiv
How Do I Know If I Have Hiv
The only way to know for sure if you have HIV is to get tested. Testing is relatively simple. You can ask your health care provider for an HIV test. Many medical clinics, substance abuse programs, community health centers, and hospitals offer them too. You can also buy a home testing kit at a pharmacy or online.
To find an HIV testing location near you, use the HIV Services Locator.
HIV self-testing is also an option. Self-testing allows people to take an HIV test and find out their result in their own home or other private location. You can buy a self-test kit at a pharmacy or online. Some health departments or community-based organizations also provide self-test kits for free.
Read the U.S. Food and Drug Administrations fact sheet on the OraQuick In-Home HIV Test, the only FDA-approved in-home HIV test.
The coronavirus pandemic has made it more difficult for some people to access traditional places where HIV testing is provided. Self-testing allows people to get tested for HIV while still following stay-at-home orders and social distancing practices. Ask your local health department or HIV service organization if they offer self-testing kits.
Topics
Do People Infected With Human Immunodeficiency Virus Have An Increased Risk Of Cancer
Yes. People infected with HIV have a substantially higher risk of some types of cancer compared with uninfected people of the same age . The general term for these cancers is “HIV-associated cancers.” Three of these cancers are known as “acquired immunodeficiency syndrome -defining cancers” or “AIDS-defining malignancies”: Kaposi sarcoma, aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and cervical cancer. A diagnosis of any of these cancers in someone infected with HIV confirms a diagnosis of AIDS.
Compared with the general population, people infected with HIV are currently about 500 times more likely to be diagnosed with Kaposi sarcoma, 12 times more likely to be diagnosed with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and, among women, 3 times more likely to be diagnosed with cervical cancer .
In addition, people infected with HIV are at higher risk of several other types of cancer . These other malignancies include cancers of the anus, liver, oral cavity/pharynx, and lung, and Hodgkin lymphoma .
People infected with HIV are 19 times more likely to be diagnosed with anal cancer, 3 times as likely to be diagnosed with liver cancer, 2 times as likely to be diagnosed with lung cancer, about 2 times as likely to be diagnosed with oral cavity/pharynx cancer, and about 8 times more likely to be diagnosed with Hodgkin lymphoma compared with the general population .
Don’t Miss: Does Nba Youngboy Have Hiv
Symptoms And Stages Of Hiv Infection
FAST FACTS
- There are three stages of HIV infection. The symptoms vary in type and severity from person-to-person.
- Stage 1 after initial infection can feel like flu but not everyone will experience this.
- Stage 2 is when many people start to feel better and may last for 10 years or more. During this time a person may have no symptoms.
- Stage 3 is when a persons immune system is very badly damaged and can no longer fight off serious infections and illnesses.
- The earlier a person is diagnosed with HIV and starts treatment, the better their health will be over time.
- Some people dont get any symptoms during stages 1 and 2, and may not know they have the virus, but they can still pass on HIV.
The signs of HIV infection can vary in type and severity from person-to-person, and some people may not have any symptoms for many years.
The stages below describe how HIV infection progresses in the body if it is left untreated. Without antiretroviral treatment for HIV, the virus replicates in the body and causes more and more damage to the immune system.
However with effective treatment, you can keep the virus under control and stop it from progressing. This is why its important to start treatment as soon as possible after testing positive.
When Should You Call The Doctor If You Have Hiv Or You Think You Have Been Exposed To Hiv
There is also post-exposure prophylaxis , which is used in emergencies and should be started within 72 hours after the possible exposure. This involves taking antiretroviral therapy after this exposure. ART may be prescribed after sexual assault, or if you think you have been exposed during consensual sex or drug-taking.
If you already know you have HIV, you should follow your healthcare providers instructions on when to call. It is important to treat any type of infection, so call if you have new symptoms or things like a fever, sweating episodes, diarrhea, and so on. Its better to check with your doctor if you have any kind of symptom that worries you.
The main feature of managing AIDS is to continue to take your medicines and to fight back at opportunistic infections at the first sign of them.
Also Check: How Soon Do You Get Hiv Symptoms